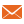
Number/percent of reporting units submitting a completed routine management information systems report on time
The extent to which an organization makes information accessible in a timely fashion.
Management information system (MIS) refers to the mechanisms and procedures for the collection and use of routine data.
"On time" means the report is received within a specified time from the end of the reporting period. Common reporting periods are "within 7 days after the start of a new month," "within 14 days of the start of a new quarter," or other set period.
As a percentage, this indicator is calculated as:
(Number of reporting units submitting a completed routine MIS report on time / total number of reporting units submitting MIS reports) x 100
Records indicating exact dates when reports were sent from a collection point and received at a unit or office where they are aggregated.
Log books; stamped and dated reports; computerized MIS databases.
This indicator provides a measure of the extent to which an organization makes information accessible in a timely fashion. The existence of complete and timely information is a pre-condition for measuring the previous indicator regarding the use of information for monitoring. The qualifier "on time" in the definition of the indicator highlights the need to monitor activities and outcomes at a pace consistent with the time frame that leaders and managers set for planning, monitoring, evaluating performance, and decision-making.
However, deadlines for submitting routine reports must be reasonable given the particular challenges to delivery. Experience in several countries has shown that pressure to submit monthly reports on time leads workers to omit some data. Thus, data are not only incomplete but also cannot be compared to data from institutions submitting figures for a full month.
Evaluators can apply this indicator to other types of reports critical to the management of reproductive health services. Such reports may be quarterly or annual performance reports (which draw on data from multiple sources), drug stock-out reports, notifiable disease or event reports, or periodic population-based reports. To be defined as "on time," a report must be received well before information is required for decision-making.
The indicator does not measure the quality of the report submitted, nor does it measure the extent to which upper level management processes the reported data in a timely manner. A complementary indicator is: Percentage of reports processed (aggregated manually or entered into a database) according to deadline.
management